| ID | Title | Difficulty | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loading... | |||
987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Hard
LeetCode
Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, calculate the vertical order traversal of the binary tree.
For each node at position (row, col), its left and right children will be at positions (row + 1, col - 1) and (row + 1, col + 1) respectively. The root of the tree is at (0, 0).
The vertical order traversal of a binary tree is a list of top-to-bottom orderings for each column index starting from the leftmost column and ending on the rightmost column. There may be multiple nodes in the same row and same column. In such a case, sort these nodes by their values.
Return the vertical order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
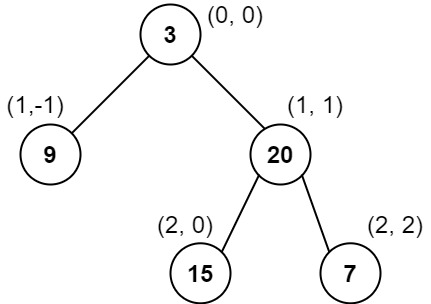
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Column -1: Only node 9 is in this column.
Column 0: Nodes 3 and 15 are in this column in that order from top to bottom.
Column 1: Only node 20 is in this column.
Column 2: Only node 7 is in this column.
Example 2:
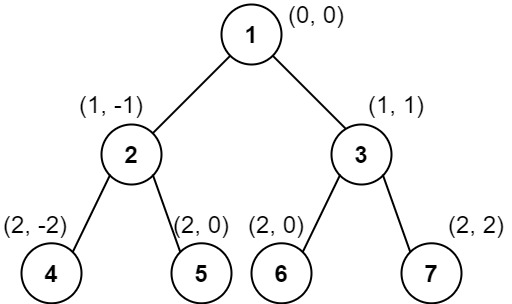
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
Column -2: Only node 4 is in this column.
Column -1: Only node 2 is in this column.
Column 0: Nodes 1, 5, and 6 are in this column.
1 is at the top, so it comes first.
5 and 6 are at the same position (2, 0), so we order them by their value, 5 before 6.
Column 1: Only node 3 is in this column.
Column 2: Only node 7 is in this column.
Example 3:
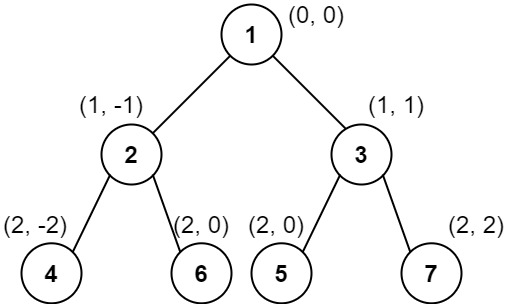
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,6,5,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
This case is the exact same as example 2, but with nodes 5 and 6 swapped.
Note that the solution remains the same since 5 and 6 are in the same location and should be ordered by their values.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
Code
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int min = 0;
int max = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return res;
helper(root, 0);
for (int i = min; i <= max; i++) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> index = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
index.offer(-min);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode curr = queue.poll();
int currIndex = index.poll();
if (!map.containsKey(currIndex)) {
map.put(currIndex, new ArrayList<>());
}
map.get(currIndex).add(curr.val);
if (curr.left != null) {
queue.offer(curr.left);
index.offer(currIndex - 1);
}
if (curr.right != null) {
queue.offer(curr.right);
index.offer(currIndex + 1);
}
}
for (Integer currIndex : map.keySet()) {
List<Integer> list = map.get(currIndex);
Collections.sort(list);
res.get(currIndex).addAll(list);
}
}
return res;
}
// 找到树的最左边和最右边
private void helper(TreeNode root, int index) {
if (root == null)
return;
min = Math.min(min, index);
max = Math.max(max, index);
helper(root.left, index - 1);
helper(root.right, index + 1);
}
}
按 <- 键看上一题!
986. Interval List Intersections
按 -> 键看下一题!
993. Cousins in Binary Tree


